
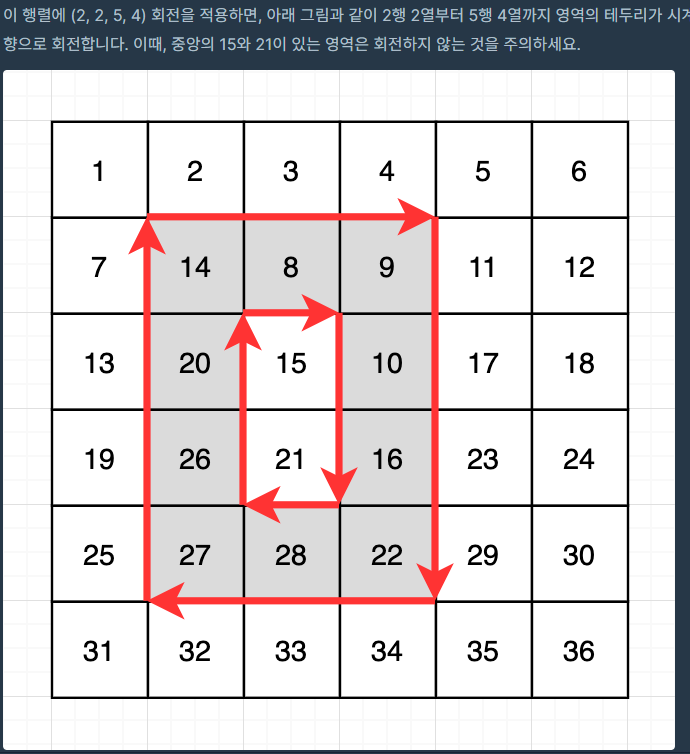
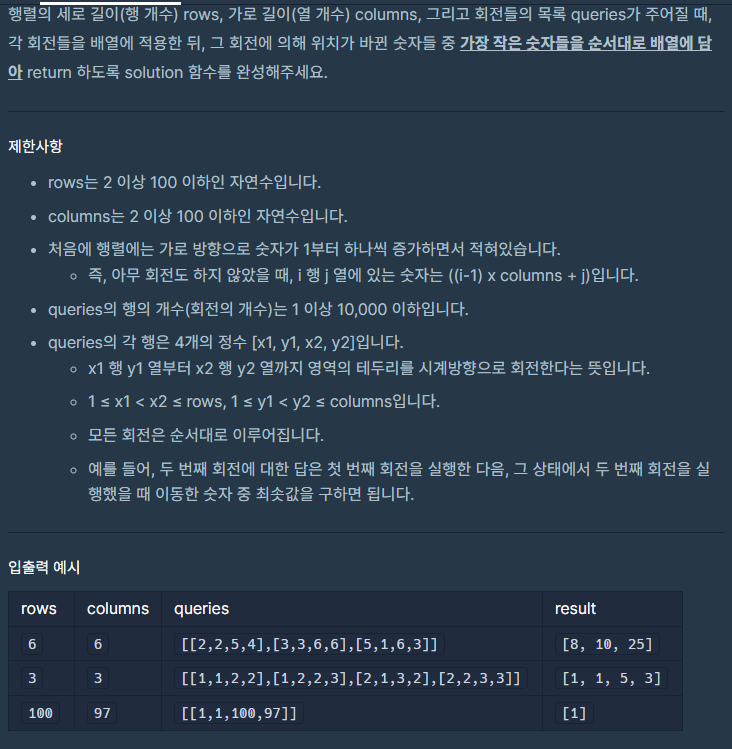
회전하는 숫자들을 저장한 뒤 회전시켜주고 그 중에서 최솟값을 정답에 저장해두면 된다.
회전하는 함수 rotate에서 기억해두어야 할 점은
정방향 반복자(begin()과 end())를 사용했다면, rotate 함수는 왼쪽 회전을 수행하고
역방향 반복자(rbegin과 rend)를 사용하여 rotate를 사용하는 이유는 nums 벡터에 대해 오른쪽 회전을 수행하기 위해서 이다.
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int board[101][101];
using namespace std;
vector<int> solution(int rows, int columns, vector<vector<int>> queries) {
vector<int> answer;
int cnt = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++) { //숫자판 초기화
for (int j = 1; j <= columns; j++) {
board[i][j] = cnt;
cnt++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); i++) {
vector<int> nums; //돌릴 숫자를 저장
vector<pair<int, int>> xy; //숫자들의 좌표값을 저장
int mn = 1e9;
int sty = queries[i][0]; //시작,끝 좌표
int stx = queries[i][1];
int edy = queries[i][2];
int edx = queries[i][3];
//도는 순서대로 숫자저장 오른->아래->왼->위
//오른
for (int x = stx + 1; x <= edx; x++) {
nums.push_back(board[sty][x]);
mn = min(mn, board[sty][x]);
xy.push_back({ sty,x });
}
//아래
for (int y = sty + 1; y <= edy; y++) {
nums.push_back(board[y][edx]);
mn = min(mn, board[y][edx]);
xy.push_back({ y,edx });
}
//왼
for (int x = edx - 1; x >= stx; x--) {
nums.push_back(board[edy][x]);
mn = min(mn, board[edy][x]);
xy.push_back({ edy,x });
}
//위
for (int y = edy - 1; y >= sty; y--) {
nums.push_back(board[y][stx]);
mn = min(mn, board[y][stx]);
xy.push_back({ y,stx });
}
rotate(nums.rbegin(), nums.rbegin() + 1, nums.rend()); //시계방향 회전
for (int x = 0; x < xy.size(); x++) {
board[xy[x].first][xy[x].second] = nums[x]; //회전한 벡터를 자리마다 대입
}
answer.push_back(mn); //최소값 저장
}
return answer;
}
'코딩테스트 > 프로그래머스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [프로그래머스][LV.2][C++]테이블 해시 함수 (2) | 2024.06.05 |
|---|---|
| [프로그래머스][LV.2][C++]미로 탈출(BFS) (1) | 2024.06.03 |
| [프로그래머스][LV 2][C++]수식 최대화 (0) | 2024.05.29 |
| [프로그래머스][LV 2][C++]괄호 변환 (0) | 2024.05.28 |
| [프로그래머스][LV 2][C++]숫자 카드 나누기 (0) | 2024.05.15 |
