
1.애니메이션 활용4(트위닝)
이제 애니메이션에서 마지막으로 트위닝이라는 것을 해보도록 하자. 트위닝이란 두 애니메이션이 바뀔때 사이에 트랜지션을 넣어주는 것 이다. 이를 위해 쉐이더 코드에서 트랜지션의 지속시간과 현재, 다음 애니메이션의 정보를 받을 수 있도록 구조체와 버퍼를 선언해주자.
TweenDemo.fx
struct TweenFrameDesc
{
float tweenDuration; //트랜지션 지속시간
float tweenRatio;
float tweenSumTime;
float padding;
KeyframeDesc curr;
KeyframeDesc next;
};
cbuffer TweenBuffer
{
TweenFrameDesc TweenFrames;
};
이렇게 한 뒤에 이제 현재 애니메이션 사이에서도 보간을 하지만 과 다음 애니메이션과 이어질때도 보간하도록 기존 함수를 수정해주자.
TweenDemo.fx
matrix GetAnimationMatrix(VertexTextureNormalTangentBlend input)
{
float indices[4] = { input.blendIndices.x, input.blendIndices.y, input.blendIndices.z, input.blendIndices.w };
float weights[4] = { input.blendWeights.x, input.blendWeights.y, input.blendWeights.z, input.blendWeights.w };
int animIndex[2];
int currFrame[2];
int nextFrame[2];
float ratio[2];
animIndex[0] = TweenFrames.curr.animIndex;
currFrame[0] = TweenFrames.curr.currFrame;
nextFrame[0] = TweenFrames.curr.nextFrame;
ratio[0] = TweenFrames.curr.ratio;
animIndex[1] = TweenFrames.next.animIndex;
currFrame[1] = TweenFrames.next.currFrame;
nextFrame[1] = TweenFrames.next.nextFrame;
ratio[1] = TweenFrames.next.ratio;
float4 c0, c1, c2, c3;
float4 n0, n1, n2, n3;
matrix curr = 0;
matrix next = 0;
matrix transform = 0;
//각 뼈의 가중치에 따른 행렬 누적
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
//처음 애니메이션
c0 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 0, currFrame[0], animIndex[0], 0));
c1 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 1, currFrame[0], animIndex[0], 0));
c2 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 2, currFrame[0], animIndex[0], 0));
c3 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 3, currFrame[0], animIndex[0], 0));
curr = matrix(c0, c1, c2, c3);
n0 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 0, nextFrame[0], animIndex[0], 0));
n1 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 1, nextFrame[0], animIndex[0], 0));
n2 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 2, nextFrame[0], animIndex[0], 0));
n3 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 3, nextFrame[0], animIndex[0], 0));
next = matrix(n0, n1, n2, n3);
matrix result = lerp(curr, next, ratio[0]);
// 다음 애니메이션
if (animIndex[1] >= 0)
{
c0 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 0, currFrame[1], animIndex[1], 0));
c1 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 1, currFrame[1], animIndex[1], 0));
c2 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 2, currFrame[1], animIndex[1], 0));
c3 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 3, currFrame[1], animIndex[1], 0));
curr = matrix(c0, c1, c2, c3);
n0 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 0, nextFrame[1], animIndex[1], 0));
n1 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 1, nextFrame[1], animIndex[1], 0));
n2 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 2, nextFrame[1], animIndex[1], 0));
n3 = TransformMap.Load(int4(indices[i] * 4 + 3, nextFrame[1], animIndex[1], 0));
next = matrix(n0, n1, n2, n3);
matrix nextResult = lerp(curr, next, ratio[1]);
result = lerp(result, nextResult, TweenFrames.tweenRatio);
}
transform += mul(weights[i], result);
}
return transform;
}
이렇게 수정해준 다음 RenderManager 클래스에서 값을 동일하게 넣어줄 수 있도록 구조체를 선언하고 생성자와 다음 애니메이션으로 교체했다면 값을 초기화 해주는 함수도 넣어주자. 그리고 이 버퍼를 초기화하고 데이터를 밀어넣는 함수도 같이 만들어주자.
RenderManager.h
struct TweenDesc
{
TweenDesc()
{
curr.animIndex = 0;
next.animIndex = -1;
}
void ClearNextAnim()
{
next.animIndex = -1;
next.currFrame = 0;
next.nextFrame = 0;
next.sumTime = 0;
tweenSumTime = 0;
tweenRatio = 0;
}
float tweenDuration = 1.0f;
float tweenDuration = 1.0f;
float tweenRatio = 0.f;
float tweenSumTime = 0.f;
float padding = 0.f;
KeyframeDesc curr;
KeyframeDesc next;
};
public:
void PushTweenData(const TweenDesc& desc);
private:
TweenDesc _tweenDesc;
shared_ptr<ConstantBuffer<TweenDesc>> _tweenBuffer;
ComPtr<ID3DX11EffectConstantBuffer> _tweenEffectBuffer;
RenderManager.cpp
void RenderManager::Init(shared_ptr<Shader> shader)
{
_tweenBuffer = make_shared<ConstantBuffer<TweenDesc>>();
_tweenBuffer->Create();
_tweenEffectBuffer = _shader->GetConstantBuffer("TweenBuffer");
}
void RenderManager::PushTweenData(const TweenDesc& desc)
{
_tweenDesc = desc;
_tweenBuffer->CopyData(_tweenDesc);
_tweenEffectBuffer->SetConstantBuffer(_tweenBuffer->GetComPtr().Get());
}
이렇게 해주고 이제 ModelAnimator의 Update부분을 수정해주면 된다. 중요한 부분은 현재 애니메이션은 진행시키고 만약 다음 애니메이션이 예약되어 있다면 두 애니메이션을 섞어서 재생해주면 된다.
ModelAnimator.cpp
void ModelAnimator::Update()
{
if (_model == nullptr)
return;
//TODO
if (_texture == nullptr)
CreateTexture();
TweenDesc& desc = _tweenDesc;
desc.curr.sumTime += DT;
//현재 애니메이션
{
shared_ptr<ModelAnimation> currentAnim = _model->GetAnimationByIndex(desc.curr.animIndex);
if (currentAnim)
{
float timePerFrame = 1 / (currentAnim->frameRate * desc.curr.speed);
if (desc.curr.sumTime >= timePerFrame)
{
desc.curr.sumTime = 0;
desc.curr.currFrame = (desc.curr.currFrame + 1) % currentAnim->frameCount;
desc.curr.nextFrame = (desc.curr.currFrame + 1) % currentAnim->frameCount;
}
desc.curr.ratio = (desc.curr.sumTime / timePerFrame);
}
}
// 다음 애니메이션이 예약 되어 있다면
if (desc.next.animIndex >= 0)
{
desc.tweenSumTime += DT;
desc.tweenRatio = desc.tweenSumTime / desc.tweenDuration;
if (desc.tweenRatio >= 1.f)
{
// 애니메이션 교체 성공
desc.curr = desc.next;
desc.ClearNextAnim();
}
else
{
// 교체중
shared_ptr<ModelAnimation> nextAnim = _model->GetAnimationByIndex(desc.next.animIndex);
desc.next.sumTime += DT;
float timePerFrame = 1.f / (nextAnim->frameRate * desc.next.speed);
if (desc.next.ratio >= 1.f)
{
desc.next.sumTime = 0;
desc.next.currFrame = (desc.next.currFrame + 1) % nextAnim->frameCount;
desc.next.nextFrame = (desc.next.currFrame + 1) % nextAnim->frameCount;
}
desc.next.ratio = desc.next.sumTime / timePerFrame;
}
}
//Anim Update
ImGui::InputInt("AnimIndex", &desc.curr.animIndex);
_keyframeDesc.animIndex %= _model->GetAnimationCount();
//다음 애니메이션 골라주기
static int32 nextAnimIndex = 0;
if (ImGui::InputInt("NextAnimIndex", &nextAnimIndex))
{
nextAnimIndex %= _model->GetAnimationCount();
desc.ClearNextAnim(); // 기존꺼 밀어주기
desc.next.animIndex = nextAnimIndex;
}
if (_model->GetAnimationCount() > 0)
desc.curr.animIndex %= _model->GetAnimationCount();
ImGui::InputFloat("Speed", &desc.curr.speed, 0.5f, 4.f);
//애니메이션 현재 프레임 정보
RENDER->PushTweenData(desc);
//SRV를 전달
_shader->GetSRV("TransformMap")->SetResource(_srv.Get());
//Bones -> shader
BoneDesc boneDesc;
const uint32 boneCount = _model->GetBoneCount();
for (uint32 i = 0; i < boneCount; i++)
{
shared_ptr<ModelBone> bone = _model->GetBoneByIndex(i);
boneDesc.transforms[i] = bone->transform;
}
RENDER->PushBoneData(boneDesc);
//Transform
auto world = GetTransform()->GetWorldMatrix();
RENDER->PushTransformData(TransformDesc{ world });
const auto& meshes = _model->GetMeshes();
for (auto& mesh : meshes)
{
if (mesh->material)
mesh->material->Update();
//BoneIndex
_shader->GetScalar("BoneIndex")->SetInt(mesh->boneIndex);
uint32 stride = mesh->vertexBuffer->GetStride();
uint32 offset = mesh->vertexBuffer->GetOffset();
//각 매쉬를 버퍼에 할당
DC->IASetVertexBuffers(0, 1, mesh->vertexBuffer->GetComPtr().GetAddressOf(), &stride, &offset);
DC->IASetIndexBuffer(mesh->indexBuffer->GetComPtr().Get(), DXGI_FORMAT_R32_UINT, 0);
_shader->DrawIndexed(0, _pass, mesh->indexBuffer->GetCount(), 0, 0);
}
}
이렇게 해주면 이제 자연스럽게 애니메이션이 변경되는 모습을 볼 수 있다.
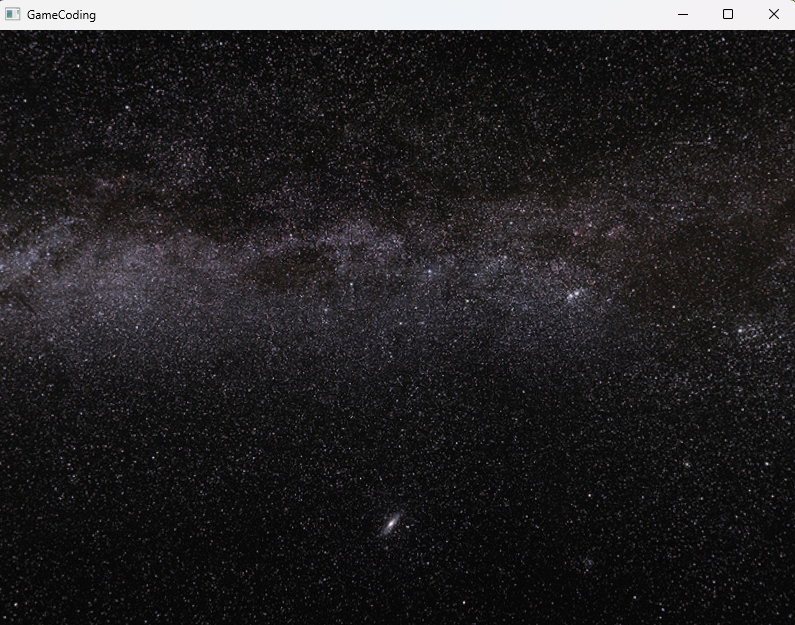
2.Sky Box
이제 하늘을 보이도록 만들어보자. 하늘을 보이게 하는 방법은 첫번째는 하늘을 큐브 모양의 형태로 만들어 준 다음에 큐브 모양을 카메라를 따라 다니게 붙여주면 된다. 지금은 조금 더 쉽게 구 형태로 만들어보자.
그리고 이 구가 엄청 멀리 있을 텐데 그 만큼 멀리있는 물체가 있을 때 그 물체도 보이게끔 처리해야한다. 그리고 이 구를 엄청 크게 한다고 해도 뒷면이라서 보이지 않기 때문에 이 부분도 처리를 해주어야한다.
Global.fx
RasterizerState FrontCounterClockwiseTrue
{
FrontCounterClockwise = true;
};카메라의 거의 끝에 구가 위치해야하는데 이 처리는 쉐이더쪽에서 하늘쪽을 그릴때만 깊이를 1에 가깝게 세팅해준다.
그리고 구를 쉐이더에서 처리해줄 때 카메라와 같은 위치에 원점이 있어야하기 때문에 월드변환을 스킵해준다.
이때 화면을 회전했을 때 자연스럽게 보이기 위해 회전의 값은 적용하려고 하면 4*4 행렬에서 마지막을 0으로 밀어주면 된다.
이때 투영화와 Rasterizer 단계를 w 값을 나눠주는데 이를 통해 깊이값이 0~1사이로 바뀌게 된다. 이때 투영단계에서 w값에 1의 근사값을 곱해주면 깊이가 카메라의 끝에 위치하게 되기 때문에 저 멀리에 있게 보인다.
SkyDemo.fx
#include "00. Global.fx"
#include "00. Light.fx"
struct VS_OUT
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD;
};
VS_OUT VS(VertexTextureNormalTangent input)
{
VS_OUT output;
// Local -> World -> View -> Projection
float4 viewPos = mul(float4(input.position.xyz, 0), V);
//투영좌표
float4 clipSpacePos = mul(viewPos, P);
output.position = clipSpacePos.xyzw;
//
output.position.z = output.position.w * 0.999999f;
output.uv = input.uv;
return output;
}
float4 PS(VS_OUT input) : SV_TARGET
{
float4 color = DiffuseMap.Sample(LinearSampler, input.uv);
return color;
}
technique11 T0
{
pass P0
{
SetRasterizerState(FrontCounterClockwiseTrue);
SetVertexShader(CompileShader(vs_5_0, VS()));
SetPixelShader(CompileShader(ps_5_0, PS()));
}
};
이렇게 해주고 이제 하늘에 해당하는 Texture를 Material로 Load하고 구를 만들어주면 된다.
SkyDemo.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include "SkyDemo.h"
#include "GeometryHelper.h"
#include "Camera.h"
#include "GameObject.h"
#include "CameraScript.h"
#include "MeshRenderer.h"
#include "Mesh.h"
#include "Material.h"
#include "Model.h"
#include "ModelRenderer.h"
#include "ModelAnimator.h"
void SkyDemo::Init()
{
RESOURCES->Init();
_shader = make_shared<Shader>(L"18. SkyDemo.fx");
// Material
{
shared_ptr<Material> material = make_shared<Material>();
material->SetShader(_shader);
auto texture = RESOURCES->Load<Texture>(L"Sky", L"..\\Resources\\Textures\\Sky01.jpg");
material->SetDiffuseMap(texture);
MaterialDesc& desc = material->GetMaterialDesc();
desc.ambient = Vec4(1.f);
desc.diffuse = Vec4(1.f);
desc.specular = Vec4(1.f);
RESOURCES->Add(L"Sky", material);
}
{
// Object
_obj = make_shared<GameObject>();
_obj->GetOrAddTransform();
_obj->AddComponent(make_shared<MeshRenderer>());
{
auto mesh = RESOURCES->Get<Mesh>(L"Sphere");
_obj->GetMeshRenderer()->SetMesh(mesh);
}
{
auto material = RESOURCES->Get<Material>(L"Sky");
_obj->GetMeshRenderer()->SetMaterial(material);
}
}
// Camera
_camera = make_shared<GameObject>();
_camera->GetOrAddTransform()->SetPosition(Vec3{ 0.f, 0.f, -5.f });
_camera->AddComponent(make_shared<Camera>());
_camera->AddComponent(make_shared<CameraScript>());
RENDER->Init(_shader);
}
void SkyDemo::Update()
{
_camera->Update();
RENDER->Update();
{
LightDesc lightDesc;
lightDesc.ambient = Vec4(0.4f);
lightDesc.diffuse = Vec4(1.f);
lightDesc.specular = Vec4(0.f);
lightDesc.direction = Vec3(1.f, 0.f, 1.f);
RENDER->PushLightData(lightDesc);
}
{
_obj->Update();
}
}
void SkyDemo::Render()
{
}

만약 깊이를 정해주는 부분에서 1로 밀어주게 되면
output.position.z = output.position.w * 0.999999f;이 부분을 그냥 w만 곱해주면 깊이 테스트에서 최대값인 1로 같기때문에 그려주지 않는다.
만약 월드, 뷰포트 변환 행렬은 스킵하게 된다면
// Local -> World -> View -> Projection
float4 viewPos = mul(float4(input.position.xyz, 0), V);우리가 아무리 회전을 해도 한 곳만 바라보게 된다. 프로젝션 연산에서 Z값은 w값에 세이브해두고 레스터라이저단계에서 나눠주는 것으로 -1 ~ 1 0~1로 설정해주게 된다.
'게임공부 > Directx11' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Directx11][C++][3D]18. 인스턴싱(MeshRenderer,ModelRenderer) (0) | 2024.09.24 |
|---|---|
| [Directx11][C++][3D]17. 인스턴싱과 드로우콜 (1) | 2024.09.23 |
| [Directx11][C++][3D]15. 애니메이션(활용2~3) (0) | 2024.09.19 |
| [Directx11][C++][3D]14. 애니메이션(데이터추출& 활용1) (0) | 2024.09.17 |
| [Directx11][C++][3D]13. 애니메이션(이론& 스키닝) (1) | 2024.09.16 |
