7.GameObject
이제 기본적인 파이프라인에 관한 것은 클래스로 만들어 뒀으니
이제 기본적인 GameObject클래스를 만들어서 물건에 종속적인 변수들을 선언해두고 앞으로 물체를 나타내고 싶을 때 이 클래스를 상속받아 사용할 수 있게 하자.
그리고 동일한 물체끼리는 묶어서 계산하고 SRT를 제외한 것은 공통으로 관리하게 하는 것이 좋다.
GameObject.h
#pragma once
class GameObject
{
public:
GameObject(ComPtr<ID3D11Device> device, ComPtr<ID3D11DeviceContext> deviceContext);
~GameObject();
void Update();
void Render(shared_ptr<Pipeline> pipeline);
private:
ComPtr<ID3D11Device> _device;
//기하학적 도형 - cpu
//vector<Vertex> _vertices;
//vector<uint32> _indices;
shared_ptr<Geometry<VertexTextureData>> _geometry;
shared_ptr<VertexBuffer> _vertexBuffer;
//인덱스버퍼 - 이거도 Geometry에 포함
shared_ptr<IndexBuffer> _indexBuffer;
shared_ptr<InputLayout> _inputLayout;
//VS
shared_ptr<VertexShader> _vertexShader;
//RS
shared_ptr<RasterizerState> _rasterizerState;
//PS
shared_ptr<PixelShader> _pixelShader;
//SRV - 이미지를 어떻게 쓸것인가 - 텍스처
shared_ptr<Texture> _texture1;
shared_ptr<SamplerState> _samplerState;
shared_ptr<BlendState> _blendState;
private:
//SRT scale, rotate translate
//쉐이더단계에서 더해줄 수 있는 인자같은 존재
TransformData _transformData;
shared_ptr<ConstantBuffer<TransformData>> _constantBuffer;
Vec3 _localposition = { 0.f,0.f,0.f };
Vec3 _localRotation = { 0.f,0.f,0.f };
Vec3 _localScale = { 1.f,1.f,1.f };
};
GameObject.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include "GameObject.h"
GameObject::GameObject(ComPtr<ID3D11Device> device, ComPtr<ID3D11DeviceContext> deviceContext)
:_device(device)
{
//정점정보 - 사각형 만들기
_geometry = make_shared<Geometry<VertexTextureData>>();
GeometryHelper::CreateRectangle(_geometry);
//정점버퍼
_vertexBuffer = make_shared<VertexBuffer>(device);
_vertexBuffer->Create(_geometry->GetVertices());
//IndexBuffer
_indexBuffer = make_shared<IndexBuffer>(device);
_indexBuffer->Create(_geometry->GetIndices());
_vertexShader = make_shared<VertexShader>(device);
_vertexShader->Create(L"Default.hlsl", "VS", "vs_5_0");
//인풋레이아웃
/// <summary>
/// 입력이 어떻게 이뤄져있는지
/// </summary>
_inputLayout = make_shared<InputLayout>(device);
_inputLayout->Create(VertexTextureData::descs, _vertexShader->GetBlob());
_pixelShader = make_shared<PixelShader>(device);
_pixelShader->Create(L"Default.hlsl", "PS", "ps_5_0");
_rasterizerState = make_shared<RasterizerState>(device);
_rasterizerState->Create();
_blendState = make_shared<BlendState>(device);
_blendState->Create();
_constantBuffer = make_shared<ConstantBuffer<TransformData>>(device, deviceContext);
_constantBuffer->Create();
_texture1 = make_shared<Texture>(device);
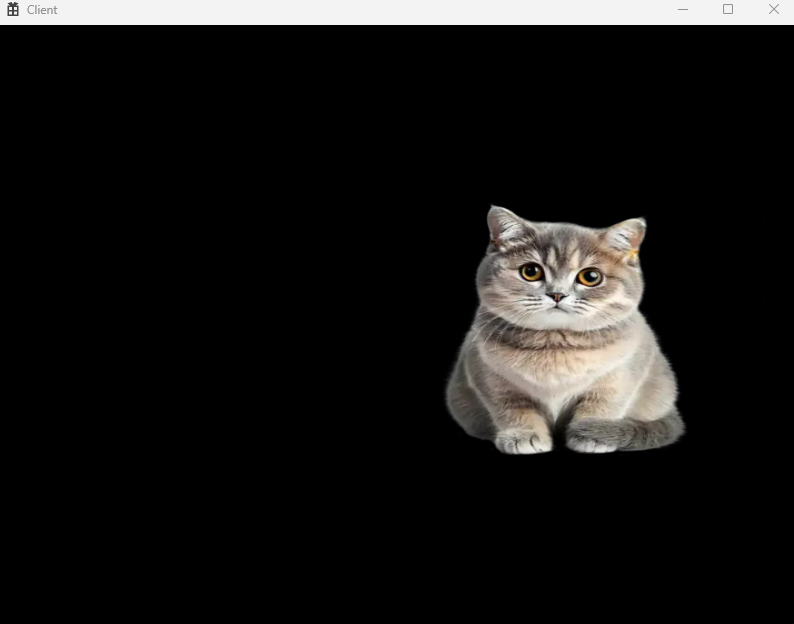
_texture1->Create(L"cat.png");
_samplerState = make_shared<SamplerState>(device);
_samplerState->Create();
}
GameObject::~GameObject()
{
}
void GameObject::Update()
{
_localposition.x += 0.001f;
//크기 회전 이동
Matrix matScale = Matrix::CreateScale(_localScale / 3);
Matrix matRotation = Matrix::CreateRotationX(_localRotation.x);
matRotation *= Matrix::CreateRotationY(_localRotation.y);
matRotation *= Matrix::CreateRotationZ(_localRotation.z);
Matrix matTranslation = Matrix::CreateTranslation(_localposition);
Matrix matWorld = matScale * matRotation * matTranslation; //SRT
_transformData.matWorld = matWorld;
_constantBuffer->CopyData(_transformData);
}
void GameObject::Render(shared_ptr<Pipeline> pipeline)
{
PipelineInfo info;
info.inputLayout = _inputLayout;
info.vertexShader = _vertexShader;
info.pixelShader = _pixelShader;
info.rasterizerState = _rasterizerState;
info.blendState = _blendState;
pipeline->UpdatePipeline(info);
pipeline->SetVertexBuffer(_vertexBuffer);
pipeline->SetIndexBuffer(_indexBuffer);
pipeline->SetConstantBuffer(0, SS_VertexShader, _constantBuffer);
pipeline->SetTexture(0, SS_PixelShader, _texture1);
pipeline->SetSamplerState(0, SS_PixelShader, _samplerState);
pipeline->DrawIndexed(_geometry->GetIndexCount(), 0, 0);
}
이제 이에 맞게 메인 코드도 수정해주자
이제 메인코드에는 그래픽, 파이프라인, 물체에 대한 포인터변수를 가지고 있고 이를 활용하는 방식으로 작동하게 된다.
제일 처음의 코드보다 훨씬 간결해졌다.
Game.h
#pragma once
#include "Graphics.h"
#include "GameObject.h"
class Game
{
public:
Game();
~Game();
public:
void Init(HWND hwnd); //윈도우 핸들받아줌
void Update();
void Render();
private:
HWND _hwnd;
shared_ptr<Graphics> _graphics;
shared_ptr<Pipeline> _pipeline;
shared_ptr<GameObject> _gameObject;
};Game.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include "Game.h"
Game::Game()
{
}
Game::~Game()
{
}
void Game::Init(HWND hwnd)
{
_hwnd = hwnd;
_graphics = make_shared<Graphics>(hwnd);
_pipeline = make_shared<Pipeline>(_graphics->GetDeviceContext());
//GO
_gameObject = make_shared<GameObject>(_graphics->GetDevice(), _graphics->GetDeviceContext());
}
void Game::Update()
{
_gameObject->Update();
}
void Game::Render()
{
_graphics->RenderBegin(); //초기화
auto _deviceContext = _graphics->GetDeviceContext();
// IA - VS - RS - PS -OM
//TODO : 그리기
{
_gameObject->Render(_pipeline);
}
_graphics->RenderEnd(); //제출
}정상 작동하는 것을 볼 수 있다.

8.Transform
게임엔진에서 상대좌표와 절대좌표를 이동시킬 떄 사용하는 것이 Transform이다
이 Transform은 계층구조에 따라 바뀔 수 있다. 예를 들어 만약 한 오브젝트의 절대좌표가 고정되어 있다고 할때
이 오브젝트가 한 오브젝트의 자식오브젝트로 들어가게 된다고 했을 때
부모가 회전이나 이동 스케일변환을 한 오브젝트라면 자식오브젝트또한 이 변환에 맞춰서 Transform이 바뀌게 된다.
이때의 Transform은 상대좌표로 표시되는 것이다.
이러한 부분을 코드로 구현해보자
GameObject의 Transform과 같은 구성요소 관리해줄 Component클래스를 만들어주고
구성요소 역활을 하게 될 Transform 클래스를 만들어주자
※※회전 연산에서 Vec3를 계속사용하다보면 축이 꼬이는 문제가 발생할 수 도 있다 -> 짐벌락 문제 -> Quaternion사용
Component.h
#pragma once
class GameObject;
class Component
{
public:
Component();
virtual ~Component();
virtual void Init() abstract;
virtual void Update() abstract;
shared_ptr<GameObject> GetGameObject() { return _owner.lock(); }
protected:
weak_ptr<GameObject> _owner;
};
Transform.h
#pragma once
#include "Component.h"
class Transform: public Component
{
public:
Transform();
~Transform();
virtual void Init() override;
virtual void Update() override;
void UpdateTransform();
//Local
Vec3 GetLocalScale() { return _localScale; }
void SetLocalScale(const Vec3& localScale) { _localScale = localScale; UpdateTransform(); }
Vec3 GetLocalRotation() { return _localRotation; }
void SetLocalRotation(const Vec3& localRotation) { _localRotation = localRotation; UpdateTransform();}
Vec3 GetLocalPosition() { return _localposition; }
void SetLocalPosition(const Vec3& localPosition) { _localposition = localPosition; UpdateTransform();}
//World
Vec3 GetScale() { return _scale; }
void SetScale(const Vec3& worldScale);
Vec3 GetRotation() { return _rotation; }
void SetRotation(const Vec3& worldRotation);
Vec3 GetPosition() { return _position; }
void SetPosition(const Vec3& worldPosition);
Matrix GetWorldMatrix() { return _matWorld; }
//계층관계
bool HasParent() { return _parent != nullptr; }
shared_ptr<Transform> GetParent() { return _parent; }
void SetParent(shared_ptr<Transform> parent) { _parent = parent; }
const vector<shared_ptr<Transform>>& GetChildren() { return _children; }
void AddChild(shared_ptr<Transform> child) { _children.push_back(child); }
private:
//SRT
Vec3 _localScale = { 1.f,1.f,1.f };
Vec3 _localRotation = { 0.f,0.f,0.f };
Vec3 _localposition = { 0.f,0.f,0.f };
//Cache
//항등행렬
Matrix _matLocal = Matrix::Identity;
Matrix _matWorld = Matrix::Identity;
Vec3 _scale;
Vec3 _rotation;
Vec3 _position;
Vec3 _right;
Vec3 _up;
Vec3 _look;
private:
//부모 오브젝트
shared_ptr<Transform> _parent;
//자식오브젝트
vector<shared_ptr<Transform>> _children;
};
Transform.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include "Transform.h"
Transform::Transform()
{
}
Transform::~Transform()
{
}
void Transform::Init()
{
}
void Transform::Update()
{
}
Vec3 ToEulerAngles(Quaternion q) {
Vec3 angles;
// roll (x-axis rotation)
double sinr_cosp = 2 * (q.w * q.x + q.y * q.z);
double cosr_cosp = 1 - 2 * (q.x * q.x + q.y * q.y);
angles.x = std::atan2(sinr_cosp, cosr_cosp);
// pitch (y-axis rotation)
double sinp = 2 * (q.w * q.y - q.z * q.x);
if (std::abs(sinp) >= 1)
angles.y = std::copysign(3.14159f / 2, sinp); // use 90 degrees if out of range
else
angles.y = std::asin(sinp);
// yaw (z-axis rotation)
double siny_cosp = 2 * (q.w * q.z + q.x * q.y);
double cosy_cosp = 1 - 2 * (q.y * q.y + q.z * q.z);
angles.z = std::atan2(siny_cosp, cosy_cosp);
return angles;
}
void Transform::UpdateTransform()
{
//크기 회전 이동
Matrix matScale = Matrix::CreateScale(_localScale);
Matrix matRotation = Matrix::CreateRotationX(_localRotation.x);
matRotation *= Matrix::CreateRotationY(_localRotation.y);
matRotation *= Matrix::CreateRotationZ(_localRotation.z);
Matrix matTranslation = Matrix::CreateTranslation(_localposition);
//로컬좌표에서의 SRT변환행렬
_matLocal = matScale * matRotation * matTranslation;
if (HasParent())
{
_matWorld = _matLocal * _parent->GetWorldMatrix();
}
else
{
//부모가 없을때는 로컬좌표가 월드좌표
_matWorld = _matLocal;
}
Quaternion quat;
_matWorld.Decompose(_scale, quat, _position);
_rotation = ToEulerAngles(quat);
// v[x y z ?]
//방식1.TransformCoor
//방식2.TransformNormal- 방향만
_right = Vec3::TransformNormal(Vec3::Right, _matWorld);
_up = Vec3::TransformNormal(Vec3::Up, _matWorld);
//라이브러리-오른손좌표계- 반대로사용해야한다.
_look = Vec3::TransformNormal(Vec3::Backward, _matWorld);
//자식계층 관리
for (const shared_ptr<Transform>& child : _children)
child->UpdateTransform();
}
void Transform::SetScale(const Vec3& worldScale)
{
if (HasParent())
{
Vec3 parentScale = _parent->GetScale();
Vec3 scale = worldScale;
scale.x /= parentScale.x;
scale.y /= parentScale.y;
scale.z /= parentScale.z;
SetLocalScale(scale);
}
else
{
SetLocalScale(worldScale);
}
}
void Transform::SetRotation(const Vec3& worldRotation)
{
if (HasParent())
{
Matrix inverseMatrix = _parent->GetWorldMatrix().Invert();
Vec3 rotation;
rotation.TransformNormal(worldRotation, inverseMatrix);
SetLocalRotation(rotation);
}
else
{
SetLocalRotation(worldRotation);
}
}
void Transform::SetPosition(const Vec3& worldPosition)
{
if (HasParent())
{
//부모-로컬->월드로 가는 변환행렬의 역행렬-> 월드 -> 로컬
Matrix worldToParentLocalMatrix = _parent->GetWorldMatrix().Invert();
Vec3 position;
//행렬연산
position.Transform(worldPosition, worldToParentLocalMatrix);
SetLocalPosition(position);
}
else
{
SetLocalPosition(worldPosition);
}
}
그리고 이러한 요소를 GameObject가 가지고있으면서 GameObject의 update함수 내부의 동작도 Transform을 통해 할 수 있도록 하자.
GameObject.h
#pragma once
class GameObject
{
public:
GameObject(ComPtr<ID3D11Device> device, ComPtr<ID3D11DeviceContext> deviceContext);
~GameObject();
void Update();
void Render(shared_ptr<Pipeline> pipeline);
private:
ComPtr<ID3D11Device> _device;
//기하학적 도형 - cpu
//vector<Vertex> _vertices;
//vector<uint32> _indices;
shared_ptr<Geometry<VertexTextureData>> _geometry;
shared_ptr<VertexBuffer> _vertexBuffer;
//인덱스버퍼 - 이거도 Geometry에 포함
shared_ptr<IndexBuffer> _indexBuffer;
shared_ptr<InputLayout> _inputLayout;
//VS
shared_ptr<VertexShader> _vertexShader;
//RS
shared_ptr<RasterizerState> _rasterizerState;
//PS
shared_ptr<PixelShader> _pixelShader;
//SRV - 이미지를 어떻게 쓸것인가 - 텍스처
shared_ptr<Texture> _texture1;
shared_ptr<SamplerState> _samplerState;
shared_ptr<BlendState> _blendState;
private:
//SRT scale, rotate translate
//쉐이더단계에서 더해줄 수 있는 인자같은 존재
TransformData _transformData;
shared_ptr<ConstantBuffer<TransformData>> _constantBuffer;
shared_ptr<Transform> _transform = make_shared<Transform>();
};
GameObject.cpp
void GameObject::Update()
{
Vec3 pos = _transform->GetPosition();
pos.x += 0.001f;
_transform->SetPosition(pos);
_transformData.matWorld = _transform->GetWorldMatrix();
_constantBuffer->CopyData(_transformData);
}
이렇게 하면 똑같이 작동하는 것을 볼 수 있다.

만약에 이렇게 만들어줬을 때 같은 오브젝트에서 부모와 자식관계를 동시에 설정하고 부모의 위치를 움직이는 코드를
작성했을 때, 자식의 위치또한 계속 갱신되기 때문에 같이 오브젝트가 같이 움직이게 된다.
GameObject.cpp
//Test code
_parent->AddChild(_transform);
_transform->SetParent(_parent);
void GameObject::Update()
{
Vec3 pos = _parent->GetPosition();
pos.x += 0.001f;
_parent->SetPosition(pos);
//Vec3 pos = _transform->GetPosition();
//pos.x += 0.001f;
//_transform->SetPosition(pos);
_transformData.matWorld = _transform->GetWorldMatrix();
_constantBuffer->CopyData(_transformData);
}
'게임공부 > Directx11' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Directx11][C++]14. 엔진구조-2(Scene,Resource,Render) (0) | 2024.08.20 |
|---|---|
| [Directx11][C++]13. 엔진구조-1(MeshRenderer) (0) | 2024.08.17 |
| [Directx11][C++]11. 프레임워크 제작3(Pipeline) (0) | 2024.08.12 |
| [Directx11][C++]10. 프레임워크 제작2(Shader,Rasterizer) (0) | 2024.08.08 |
| [Directx11][C++]9. 프레임워크 제작(Graphics,Input Assembler,Geometry) (0) | 2024.07.31 |
